人工智能教程 - 数学基础课程1.1 - 数学分析(一)34-35 泰勒级数
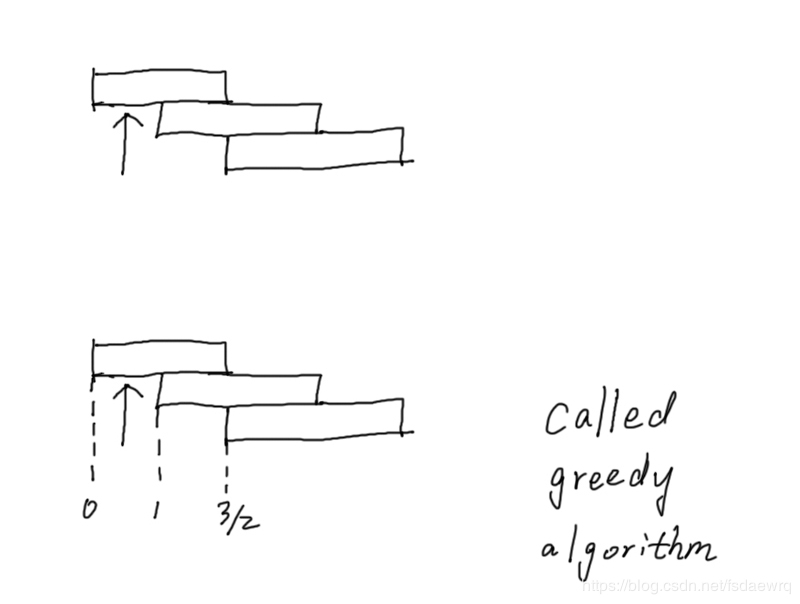
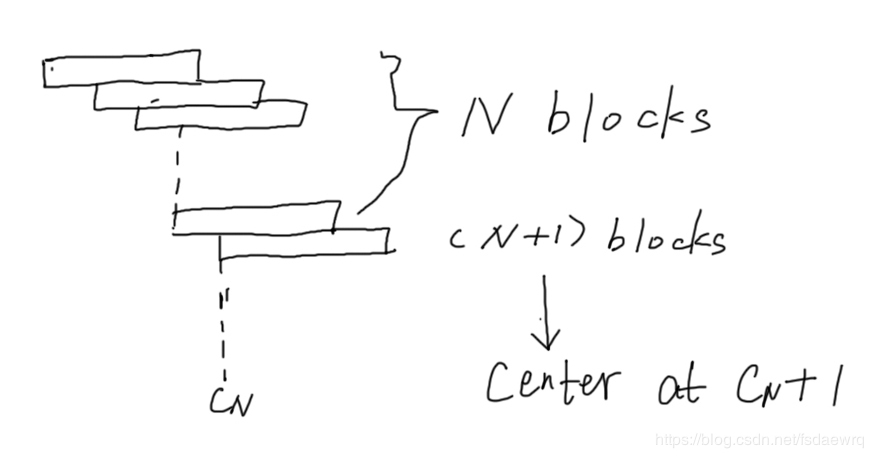
CN+1=NCN+1(CN+1)N+1−(N+1)CN+1N+1C_{N+1}=\frac{NC_N+1(C_N+1)}{N+1}-\frac{(N+1)C_N+1}{N+1}CN+1=N+1NCN+1(CN+1)−N+1(N+1)CN+1
Center of mass of N+1 blocksX-coordinate
CN+1=CN+1N+1C_{N+1}=C_N+\frac{1}{N+1}CN+1=CN+N+11C1=1C_1=1C1=1
C2=1+12C_2=1+\frac{1}{2}C2=1+21
C3=C2+13=1+12+13C_3=C_2+\frac{1}{3}=1+\frac{1}{2}+\frac{1}{3}C3=C2+31=1+21+31
CN=1+12+13+14+...+1NC_N=1+\frac{1}{2}+\frac{1}{3}+\frac{1}{4}+...+\frac{1}{N}CN=1+21+31+41+...+N1
CN=SNC_N=S_NCN=SN
lnN<SN<(lnN)+1lnN<S_N<(lnN)+1lnN<SN<(lnN)+1
as N→∞,lnN→∞ and SN→∞as \ \ N\rightarrow \infty,lnN\rightarrow \infty \ \ and \ \ S_N \rightarrow \inftyas N→∞,lnN→∞ and SN→∞
|x|<1 (geometric series)
(converge)
(1+x+x2)=S(1+x+x^2) =S(1+x+x2)=S
x+x2+x3+...=Sxx+x^2+x^3+... =Sxx+x2+x3+...=Sx
1=S−Sx=S(1−x)1=S-Sx =S(1-x)1=S−Sx=S(1−x)
where series convergence ∑anxn\sum a_nx^n∑anxn diverge
|x|>R very delicate borderline(很微妙的边界)—not used by us
∣anxn∣→0|a_nx^n|\rightarrow 0∣anxn∣→0 exponentially fast |x|<R
∣anxn∣≠→0|a_nx^n|\neq \rightarrow 0∣anxn∣=→0 for |x|>R
Rules for conergant power series are just like polynomials f(x)+g(x),f(x).g(x),f(g(x)),f(x)/g(x)ddxf(x),∫f(x)dx\frac{d}{dx}f(x),\int f(x)dxdxdf(x),∫f(x)dx
ddx(a0+a1x+a2x2+a3x3+...)=a1+2a2x+3a3x2+...\frac{d}{dx}(a_0+a_1x+a_2x^2+a_3x^3+...)=a_1+2a_2x+3a_3x^2+...dxd(a0+a1x+a2x2+a3x3+...)=a1+2a2x+3a3x2+...
∫(a0+a1x+a2x2+...)dx=c+a0+a1x2/2+a2x3/3+...\int(a_0+a_1x+a_2x^2+...)dx=c+a_0+a_1x^2/2+a_2x^3/3+...∫(a0+a1x+a2x2+...)dx=c+a0+a1x2/2+a2x3/3+...
Ex: (Euler欧拉)
| x=0 | |
|---|---|
| f(x)=exf(x)=e^xf(x)=ex | 1 |
| f′(x)=exf'(x)=e^xf′(x)=ex | 1 |
| f′′(x)=exf''(x)=e^xf′′(x)=ex | 1 |
ex=1+x+x22!+x33!+...\LARGE e^x=1+x+\frac{x^2}{2!}+\frac{x^3}{3!}+...ex=1+x+2!x2+3!x3+...
Ex2:
11+x=1−x+x2−x3+...\LARGE \frac{1}{1+x}=1-x+x^2-x^3+...1+x1=1−x+x2−x3+...
Ex3:
sin(x)=x−x33!+x55!−...\LARGE sin(x)=x-\frac{x^3}{3!}+\frac{x^5}{5!}-...sin(x)=x−3!x3+5!x5−...
New Power Series From Old 1). Multiplyxsin(x)=x2−x43!+x65!−...\LARGE xsin(x)=x^2-\frac{x^4}{3!}+\frac{x^6}{5!}-...xsin(x)=x2−3!x4+5!x6−...
2). Differentiate求导cos(x)=sin′(x)=1−3x23!+5x45!−...=1−x22+x44!−...\LARGE cos(x)=sin'(x)=1-\frac{3x^2}{3!}+\frac{5x^4}{5!}-...\LARGE =1-\frac{x^2}{2}+\frac{x^4}{4!}-...cos(x)=sin′(x)=1−3!3x2+5!5x4−...=1−2x2+4!x4−...
3). Integrate:ln(1+x)=∫0xdt1+t\LARGE ln(1+x)=\int_{0}^{x}\frac{dt}{1+t}ln(1+x)=∫0x1+tdt
(x>−1)=∫0x(1−t+t2+t3+...)dt\LARGE (x>-1)=\int_0^x(1-t+t^2+t^3+...)dt(x>−1)=∫0x(1−t+t2+t3+...)dt
=[t−t22+t33−t44+...]∣0x\LARGE =[t-\frac{t^2}{2}+\frac{t^3}{3}-\frac{t^4}{4}+...]|_0^x=[t−2t2+3t3−4t4+...]∣0x
ln(1+x)=[x−x22+x33−x44+...](R=1)\LARGE ln(1+x)=[x-\frac{x^2}{2}+\frac{x^3}{3}-\frac{x^4}{4}+...](R=1)ln(1+x)=[x−2x2+3x3−4x4+...](R=1)
4).Substitue:e−t2\LARGE e^{-t^2}e−t2(x=−t2;in ex)\LARGE (x=-t^2;in \ \ e^x)(x=−t2;in ex)
=1−t2+t42!+t63!−...\LARGE =1-t^2+\frac{t^4}{2!}+\frac{t^6}{3!}-...=1−t2+2!t4+3!t6−...
Erf(x)=2π∫0xe−t2dx=2π(x−x33+x55.2!−737.3!+...)\LARGE Er f(x)=\frac{2}{\sqrt{\pi}}\int_0^xe^{-t^2}dx\LARGE =\frac{2}{\sqrt{\pi}}(x-\frac{x^3}{3}+\frac{x^5}{5.2!}-\frac{7^3}{7.3!}+...)Erf(x)=π2∫0xe−t2dx=π2(x−3x3+5.2!x5−7.3!73+...)
作者:KuFun人工智能